Kakortokite
Category: Plutonic
Type Alkaline nepheline syenite.
Commons Kakortokite is a local name for the variety of agpaitic nephelinic syenite with distinct cumulate structure and magmatic layering consisting of recurrent bands rich in alkaline feldspar, eudialyte and arfvedsonite.
Name origin The rock is named after the town Qaqortoq in the region of Ilimaussaq of southern Greenland, where the rock was described for the first time (Le Maitre, et al., 2004).
Locality Kangerdluarssaq Fjord, the Ilímaussaq magmatic complex, Greenland (sample courtesy of M. Marks).
GPS:
Major minerals Alkaline feldspar, nepheline, aegirine, arfvedsonite.
Accessory minerals Sodalite, aenigmatite, magnetite, rinkite, fluorite, löllingite, sphalerite, galena.
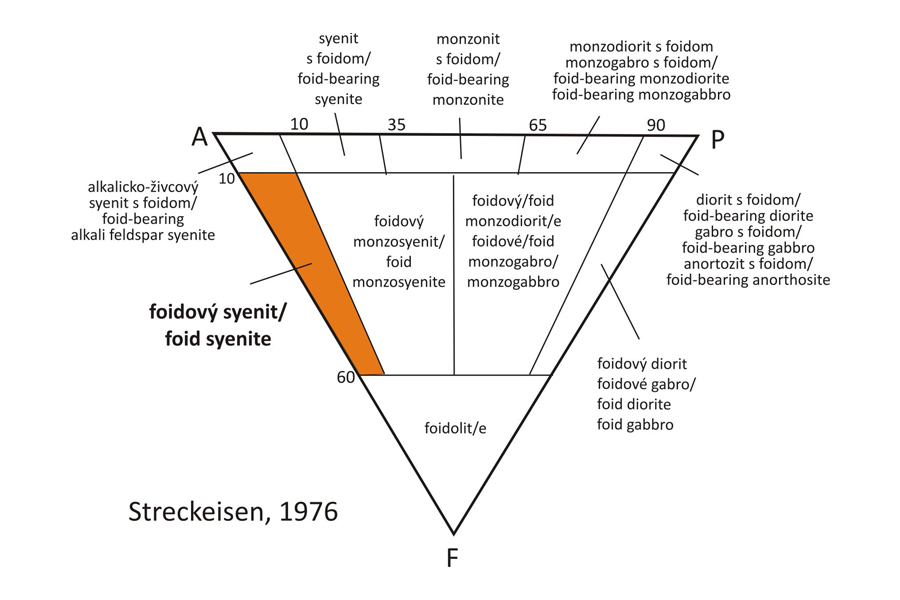
Classification The field of foid syenite is defined in QAPF diagram for plutonic rocks (Streckeisen, 1976) by the modal content of foids (F 10 – 60 %) and by the plagioclase ratio P/(P+A) from 0 to 10. The rock projects in the lower part of the classification diagram. Since the prevailing phase is nepheline, the rock is named the nepheline syenite.
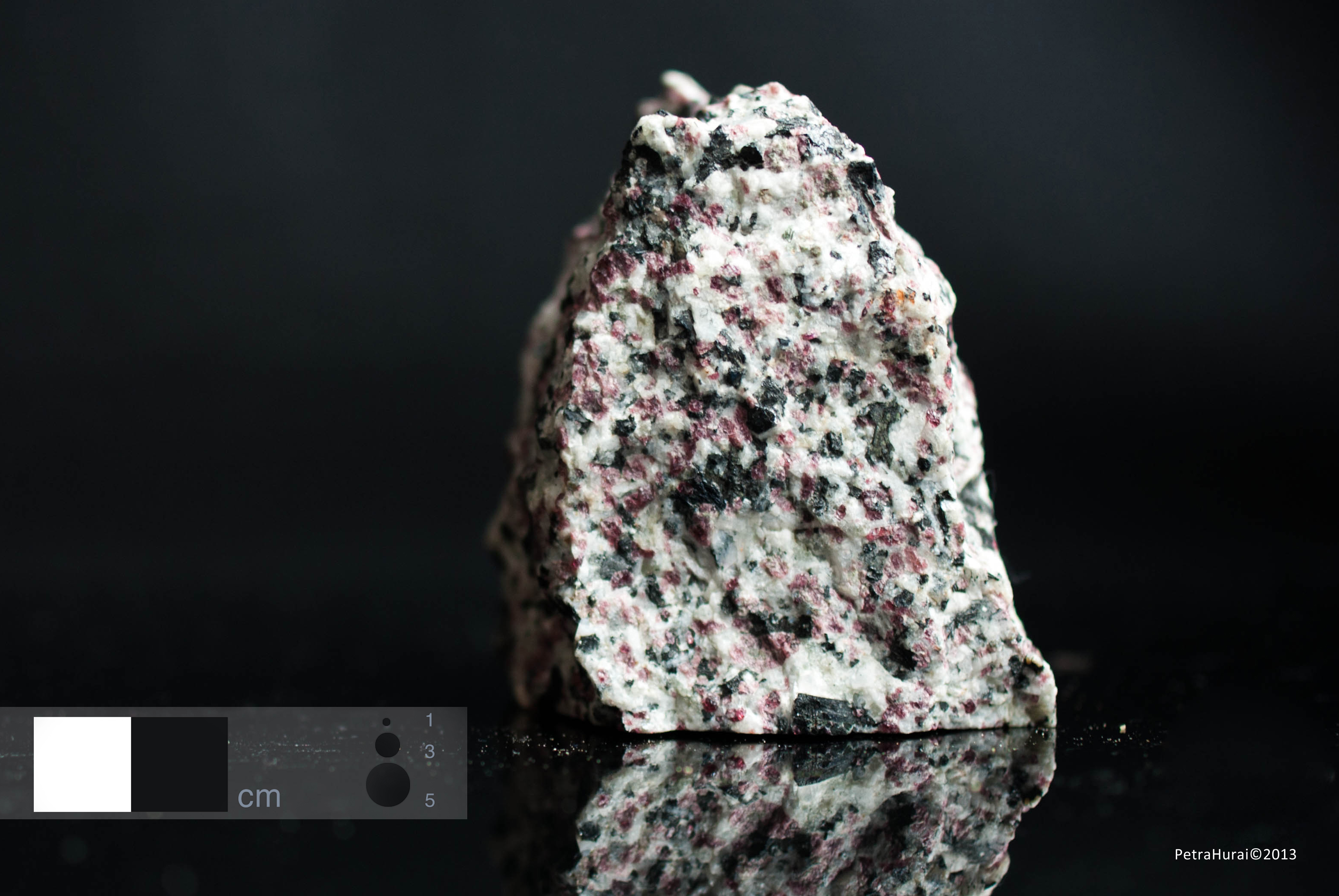

Colour Bright to white, with red grains of eudialyte.
Structure Phaneritic, layered, laminated.
Granularity Medium (1 - 3 mm) to coarse-grained (3 mm – 1 cm) rock.
Texture Phaneritic, subhedrally granular.
Alterations The rock is altered by zeolitization, it contains secondary analcime and natrolite.
Petrographic characteristics Medium-to-coarse-grained, locally layered to laminated. Periodically repeating layers are compositionally different, with variable eudialyte (pink) and arfvedsonite (black) contents. Alkaline feldspar and nepheline grains exhibit white colours. The sample shown is rich in eudialyte and is normally designated as red kakortokite. Other types are designated as black or white kakortokites according to the colour of the dominant mineral.
Usage Potentially economically important as the source of Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf, REE, Y. Limited exploratory mining and exploitation of Zr, REE/rich kakortokite and marginal pegmatite occurred in southern Greenland in 1980s.
Literature Bailey, J.C., Gwozdz, R., Rose-Hansen, J. & Sørensen, H., 2001: Geochemical overview of the Ilímaussaq alkaline complex, South Greenland. Geology of Greenland Survey Bulletin, 190, 35-53. Bohse, H., Brooks, C.K. & Kunzendorf, H., 1971: Field observations on the kakortokites of the Ilímaussaq intrusion, South Greenland, including mapping and analyses by portable Xray fluorescence equipment for zirconium and niobium. Rapport Grønlands Geologiske Undersøgelse, 38, 43 pp. Ferguson, J. 1970: The significance of the kakortokite in the evolution of the Ilímaussaq intrusion, South Greenland. Bulletin Grønlands Geologiske Undersøgelse, 89, 193 pp. Pfaff, K., Krumrei, T., Marks, M., Wenzel, T., Rudolf, T. & Markl, G., 2008: Chemical and physical evolution of the ‘lower layered sequence’ from the nepheline syenitic Ilímaussaq intrusion, South Greenland: Implications for the origin of magmatic layering in peralkaline felsic liquids Lithos, 106, 280-296. Sørensen, H., 2001: The Ilímaussaq alkaline complex, South Greenland: status of mineralogical research with new results. Geology of Greenland Survey Bulletin, 190, 23 pp.
Photomicrographs
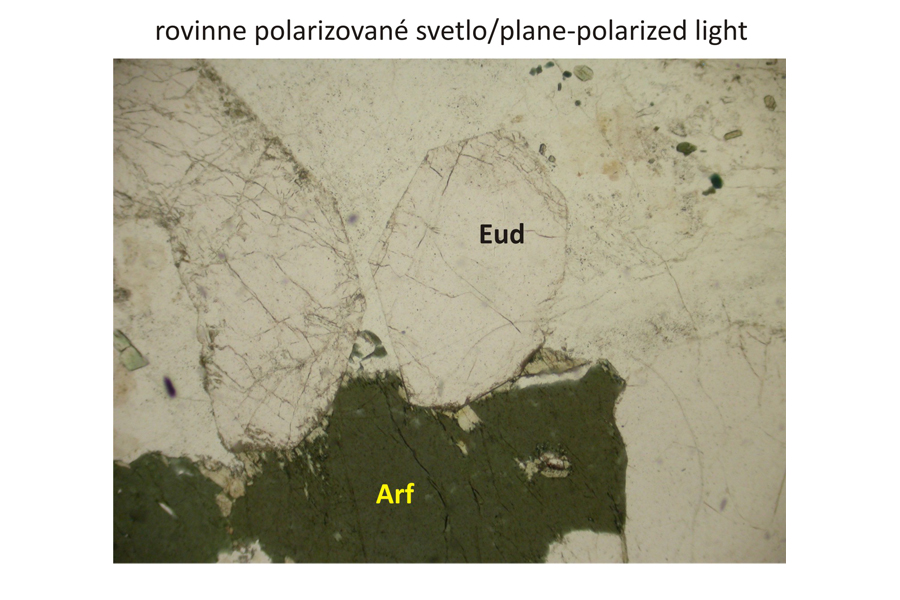

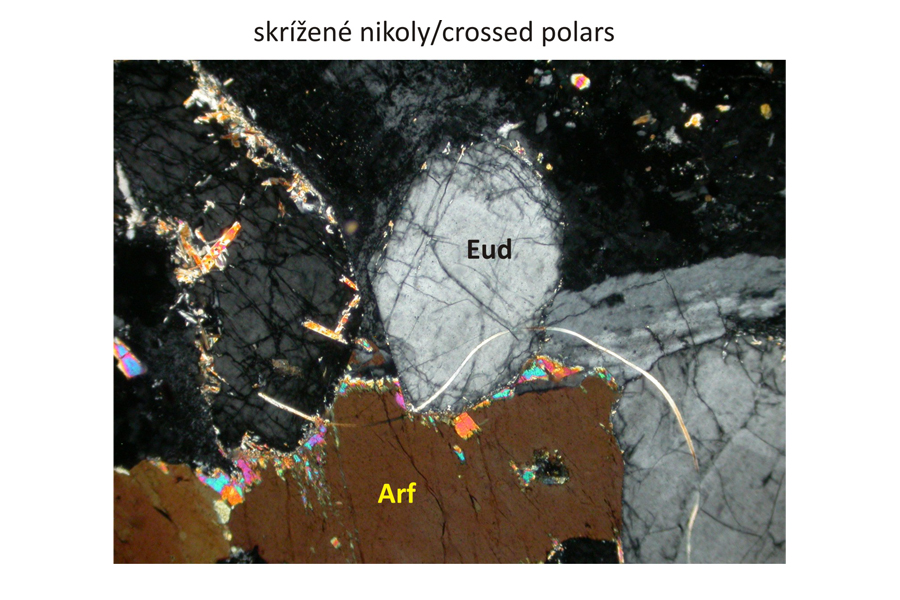
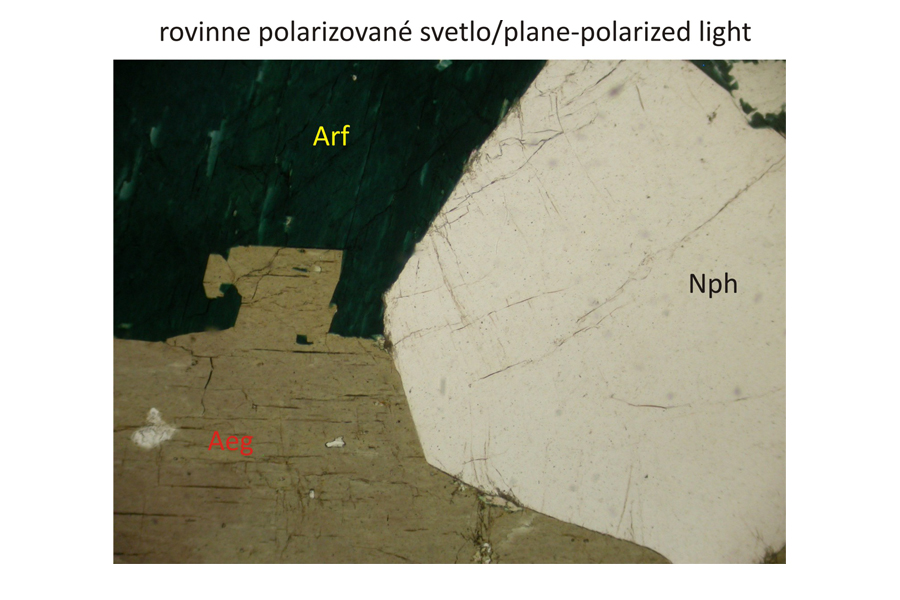
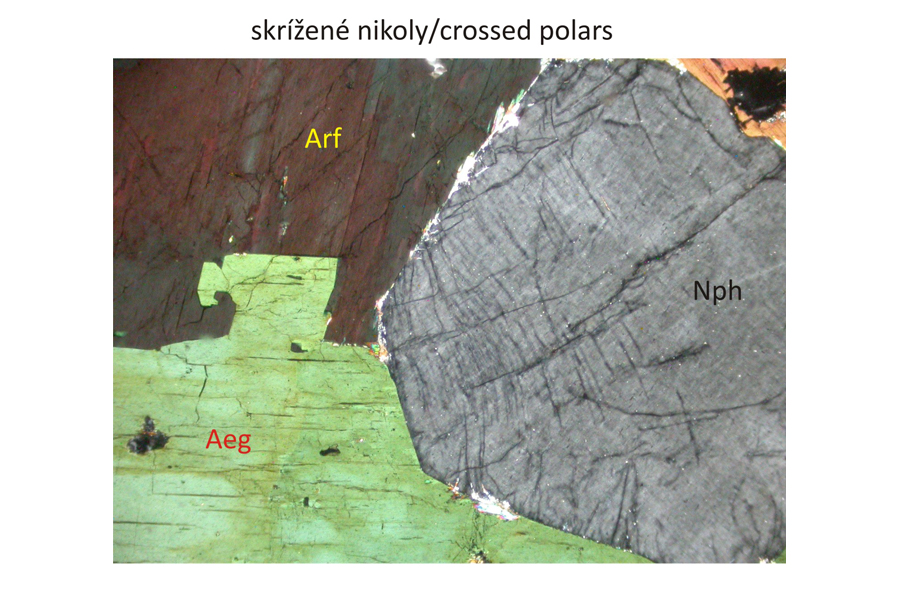
Subhedral eudialyte – Eud and arfvedsonite – Arf phenocrysts alongside alkalic feldspar. The arfvedsonite is discernible by a pronounced green pleochroism under plane-polarized light, and by high interference colours in crossed polars. Eudialyte is pale-pink to transparent, with very high relief under plane-polarized light. Under crossed polars, it has very low, grey interference colour similar to that of nepheline – Nph. The nepheline displays a low relief and basal cross-section of a hexagonal shape (lower left image). In addition, nepheline has bad cleavage compared to that of alkalic feldspars. In contrast to arfvedsonite, alkalic pyroxene – aegirine Aeg – exhibits less intense green and greenish yellow to green-brown pleochroism under plane-polarized light, and also a different style of the cleavage. Width of all photomicrographs corresponds to 2.2 mm.
Normative composition
High potassium content in red kakortokite is manifested by a high content of normative orthoclase – or. The high Na content accompanied by the lack of alumina is reflected in the normative acmite – ac and very rare normative component – sodic metasilicate – ns. The rock is unsaturated with Si and this is pronounced by the normative olivine – ol and nepheline – ne. The normative zircon – z is also diagnostic of this type of rocks.
Normative minerals
SiO2
TiO2
ZrO2
Al2O3
Fe2O3
FeO
MnO
MgO
CaO
Na2O
K2O
P2O5
F
S
CO2
Total
Molar proportion of normative mineral
Molecular mass of normative mineral
Weight % of normative mineral
Oxide
(wt. %)
52.20
0.68
2.37
10.51
6.04
6.90
0.41
0.28
3.58
9.26
3.39
0.04
0.01
0.06
95.73
Molecular
weight
60.08
79.88
123.22
101.96
159.69
71.85
70.94
40.31
56.08
61.98
94.20
141.95
32.06
44.01
Molecular
proportion
0.8688
0.0085
0.0192
0.1031
0.0378
0.1018
0.0058
0.0069
0.0638
0.1494
0.0360
0.0003
0.0003
0.0014
ap
0.0009
0.0003
0.0003
328.68
0.09
pr
0.0002
0.0003
0.0002
119.09
0.02
il
0.0085
0.0085
0.0085
151.75
1.29
cc
0.0014
0.0014
0.0014
100.09
0.14
z
0.0192
0.0192
0.0192
183.31
3.53
or
0.2159
0.0360
0.0360
0.0360
556.67
20.03
ab´
0.4026
0.0671
0.0671
0.0671
524.46
35.19
ac
0.1513
0.0378
0.0378
0.0378
462.02
17.48
ns
0.0445
0.0445
0.0445
122.07
5.43
zvyšky
0.0931
0.0069
0.0615
di
0.1231
0.0573
0.0043
0.0651
0.0651
245.91
15.13
hy´
0.0386
0.0359
0.0027
0.0386
129.74
5.00
ol
0.0193
0.0359
0.0027
0.0193
199.40
3.84
ne
0.0535
0.0267
0.0267
0.0267
284.11
7.60
ab
0.2421
0.0403
0.0403
0.0403
524.46
21.16
D: 0.1263
D1: 0.1070
D2: 0.1070
Mg/(Mg+Fe2+): 0.069
Total of normative wt. % 95.73
Comment Normative anorthite – an could not be created owing to the missing alumina, which was spent for the creation of normative orthoclase – or and albite – ab. Increased sulphur content results in the normative pyrite pr and that of zirconium in the normative zircon – z.
Chemical composition
The red kakortokite is peralkalic rock with increased Na2O and K2O, and low CaO and MgO contents. The molar ratio (Na2O + K2O)/Al2O3 is very high, corresponding to 1.8 (see table with the chemical composition). The term “agpaitic” refers to nepheline syenites with the molar ratio (Na2O + K2O)/Al2O3 > 1 accompanied by high contents of Na, F, Cl, and Zr, contrasting with low contents of Ca and Mg. This term is recently used only for peralkalic nepheline syenites with complex Zr and Ti minerals, such as eudialyte. The term agpaitic cannot be interchanged with the term peralkalic, which refers merely to the molar ratio of alkalies and alumina. Compared to Si-saturated rocks (q in norm), the red kakortokite is typical of an increased Na2O and lowered Al2O3 and SiO2 contents. Interesting are also increased Nb, Ta, Zr (up to several wt. %), Hf and Y contents. The rock is also enriched in LREE, especially La and Ce. The red kakortokite has also typically increased F and Cl contents (up to 0.5 wt. %). Black and white kakortokites are slightly chemically different from red kakortokite (see table of chemical compositions).
-
SiO2
52.20TiO2
0.68Al2O3
10.51Fe2O3
6.04FeO
6.90MnO
0.41MgO
0.28CaO
3.58Na2O
9.26K2O
3.39P2O5
0.04H2O+
2.18H2O-
0.21CO2
0.06SO3
0.02F
0.38Cl
0.30Total
98.81Mg(Mg/Fe2+)
0.03A/CNK
0.45A/NK
0.57
Bailey et al., 2001.
-
SiO2
48.06TiO2
0.57Al2O3
8.16Fe2O3
7.17FeO
17.08MnO
0.48MgO
0.58CaO
4.39Na2O
6.95K2O
2.79P2O5
0.01H2O+
1.66H2O-
0.15CO2
0.05F
2.07Cl
0.04Total
100.21Mg(Mg/Fe2+)
0.03A/CNK
0.41A/NK
0.58
-
SiO2
53.30TiO2
0.16Al2O3
13.40Fe2O3
7.90FeO
3.42MnO
0.31MgO
0.23CaO
2.10Na2O
8.84K2O
4.04P2O5
0.04H2O+
2.81H2O-
0.41CO2
0.09SO3
0.02F
1.05Cl
0.04Total
98.15Mg(Mg/Fe2+)
0.05A/CNK
0.62A/NK
0.72